PDF Chromosome Inequality Causes and Consequences of Non Biology Diagrams
BlogPDF Chromosome Inequality Causes and Consequences of Non Biology Diagrams Rearrangements arising from chromosome shattering are likely to be frequent in chromosomally unstable cells exhibiting high rates of chromosome segregation errors, especially those deficient in

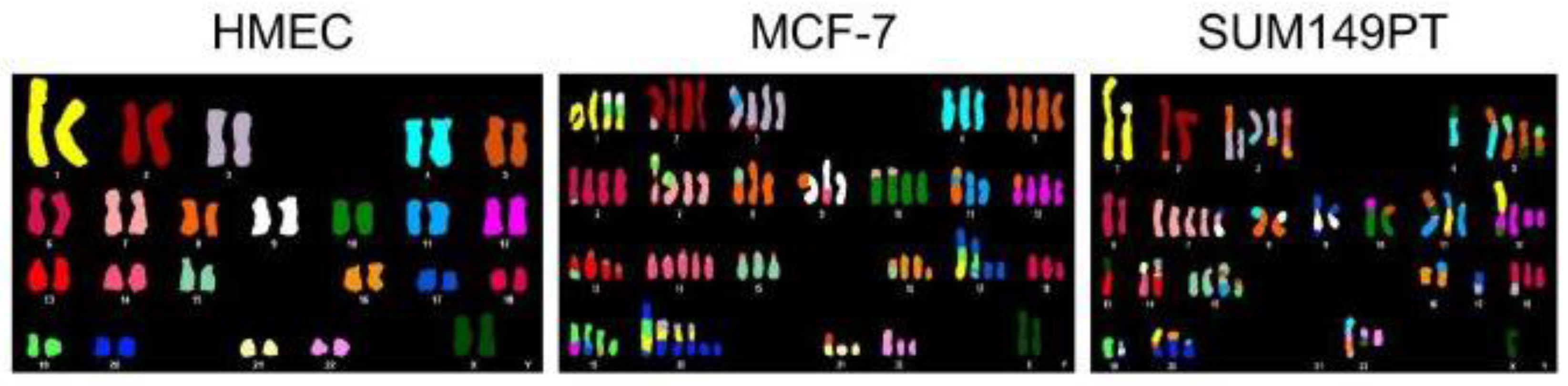
To test whether chromosome segregation errors directly provoke gross chromosomal rearrangements, Y chromosome paint probes were hybridized to metaphase spread preparations. A majority (59±8%, 92/153 metaphases) of cells examined from CEN-SELECT harbored at least one type of Y-specific structural change ( Fig. 2a ) with different alterations
The Consequences of Chromosome Segregation Errors in Mitosis and ... Biology Diagrams
Chromosome segregation errors may also involve fragments of whole chromosomes. A major consequence of segregation defects is change in the relative dosage of products from genes located on the missegregated chromosomes. Abnormal expression of transcriptional regulators can also impact genes on the properly segregated chromosomes. Chromosome segregation errors during mitotic and meiotic cell divisions give rise to aneuploidy, an abnormal number of chromosomes. Aneuploidy can be frequently detected in the genome of cancer cells 1 or individuals with developmental disorders, and is the leading cause of spontaneous miscarriages after fertilization.
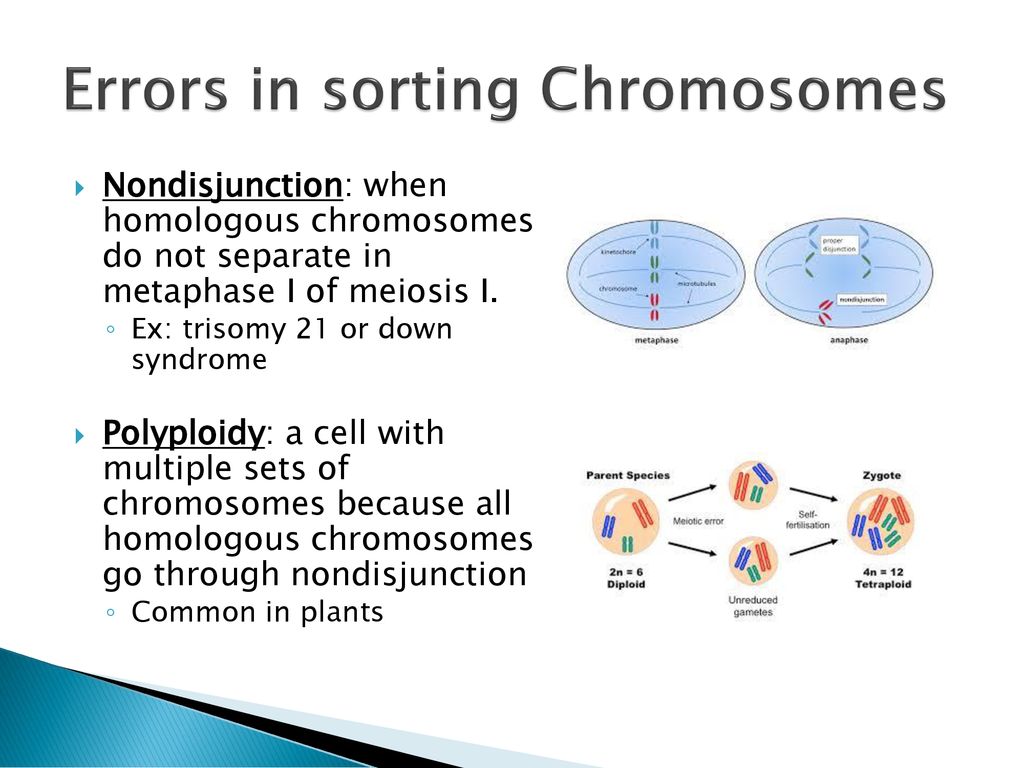
Errors in chromosome segregation are common during the mitotic divisions of preimplantation development in mammalian embryos, giving rise to so-called 'mosaic' embryos possessing a mixture of euploid and aneuploid cells. Mosaicism is widely considered to be detrimental to embryo quality and is frequently used as criteria to select embryos for transfer in human fertility clinics. Types of chromosome segregation errors. A schematic diagram illustrates the process by which numerical and structural aberrations occur during chromosome segregation. 2.1 Numerical aberrations. Numerical aberrations are defined as structural alterations to the number of chromosomes within a cell. Abnormalities in the number of chromosomes are

Chromosome Inequality: Causes and Consequences of Non Biology Diagrams
To examine the impact of chromosome segregation errors on chromosome integrity, we treated hTert-immortalized, nontransformed human retinal pigment epithelial (RPE-1) cells with Monastrol to induce formation of erroneous kinetochore-microtubule attachments, in which one kinetochore is attached to both spindle poles (3, 6).Subsequent release from the Monastrol block causes a high incidence of
